How To Do Industry Research: Porter’s Five Forces Framework
While we talk a lot about market analysis (which is super important for business growth btw), how to do industry research is equally important. Sometimes people confuse these two concepts and use them interchangeably, however market analysis and industry research are totally different concepts. Market analysis helps you to understand your market (people you are selling to) and industry research aims to understand the state of industry (set of companies who sell the same or similar products as you). That’s why industry research is mostly focused on the competitors landscape and has a purpose to figure out how easy it will be for you to compete in the market.
One powerful tool for analyzing industry dynamics is Porter’s Five Forces Framework, developed by famous economist Michael Porter. In this post, we’ll discuss how to do industry research using Porter’s Five Forces Framework effectively, so you could gain valuable insights into industry competitiveness, profitability, and strategic opportunities.
What is Porter’s Five Forces Framework
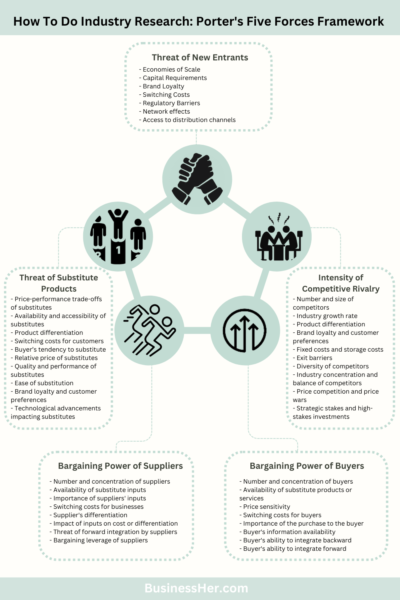
Porter’s Five Forces Framework is a strategic tool used to analyze the competitive forces within an industry and assess the attractiveness of entering or operating within that industry. The five forces identified by Porter include:
- Threat of New Entrants: This force evaluates the ease or difficulty for new competitors to enter the industry. Factors such as barriers to entry, economies of scale, and brand loyalty influence the threat of new entrants.
- Bargaining Power of Buyers: The bargaining power of buyers refers to the influence that customers wield over industry participants. Factors such as the availability of substitute products, switching costs, and buyer concentration impact buyer bargaining power.
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers: This force assesses the influence of suppliers on industry participants. Factors such as supplier concentration, switching costs, and the availability of substitute inputs determine supplier bargaining power.
- Threat of Substitute Products or Services: The threat of substitutes examines the likelihood of customers switching to alternative products or services. Factors such as price-performance trade-offs, brand loyalty, and switching costs influence the threat of substitutes.
- Intensity of Competitive Rivalry: This force evaluates the level of competition among existing industry players. Factors such as industry growth, product differentiation, and exit barriers impact competitive rivalry.
Here is how to do industry research using Porter’s Five Forces framework (click to expand):
How to Do Industry Research Using Porter’s Five Forces
- Identify Industry Participants: Begin by identifying the key players within the industry, including competitors, suppliers, buyers, and potential new entrants. Conduct research to gather information on their market share, financial performance, and strategic capabilities.
- Assess Threat of New Entrants: Evaluate the barriers to entry within the industry, such as capital requirements, regulatory specifics, and economies of scale. Consider the likelihood of new entrants disrupting the market and the potential impact on existing players.
- Analyze Bargaining Power of Buyers: Examine the factors influencing buyer bargaining power, such as the availability of substitute products, buyer concentration, and switching costs. Assess the degree to which buyers can influence pricing, terms, and conditions within the industry.
- Evaluate Bargaining Power of Suppliers: Assess the influence of suppliers on industry participants, considering factors such as supplier concentration, input costs, and the availability of substitute inputs. Determine the extent to which suppliers can dictate terms and conditions to industry players.
- Assess Threat of Substitute Products or Services: Analyze the availability and attractiveness of substitute products or services that could potentially displace industry offerings. Consider factors such as price-performance trade-offs, brand loyalty, and switching costs for customers.
- Evaluate Intensity of Competitive Rivalry: Assess the level of competition among existing industry players, considering factors such as market concentration, industry growth, and product differentiation. Identify competitive dynamics and potential areas of strategic advantage or vulnerability.
How to do industry analysis using Porter’s Five Forces framework with examples you can find here.
Conclusion
How to do industry research using Porter’s Five Forces Framework? You need to analyze the main forces of competition for your business. This way you can identify key drivers of industry profitability, assess strategic risks, and develop informed strategies to build your competitive advantage. Remember that you need to conduct industry research systematically (in combination with thorough market research), so you could always have valuable insights about the state of the industry.


















Post Comment