How to Do Business Model Canvas Analysis
The Business Model Canvas (BMC) is a strategic tool used to visualize and assess the key elements of a business model. By conducting a business model canvas analysis, companies can identify strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities within their existing model and make informed decisions for growth and innovation. This guide will walk you through the steps of performing an effective analysis, explain each component of the business model canvas, and offer actionable insights for leveraging the results.
What is Business Model Canvas Analysis?
A business model canvas analysis involves a systematic examination of the nine building blocks of the BMC. This analysis helps businesses understand how their resources, processes, and value propositions interact to meet customer needs and generate revenue. It’s a practical framework for startups, established businesses, and organizations seeking to pivot or improve their operations.
We have already written a guide on how to prepare your business model canvas, and in this article we will focus more on the analysis part.
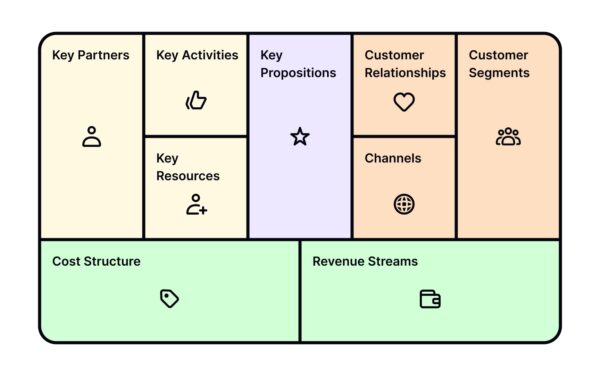
Components of the Business Model Canvas
The BMC consists of nine interconnected sections. Let’s break them down and explore how to analyze each:
1. Customer Segments
Customer segments represent the groups of people or organizations your business serves.
- Questions to Analyze:
- Who are your primary and secondary customers?
- What are their needs, preferences, and behaviors?
- Are there underserved or emerging customer segments you could target?
Example: A coffee shop may cater to busy professionals, students, and local residents, each with unique preferences.
2. Value Proposition
This describes the unique value your product or service delivers to customers.
- Questions to Analyze:
- What problems does your product solve or what needs does it fulfill?
- How does your offering differentiate itself from competitors?
- Are your value propositions still relevant to customer demands?
Example: Tesla’s value proposition includes eco-friendly transportation, advanced technology, and luxury appeal.
3. Channels
Channels are the means by which you deliver your value proposition to customers.
- Questions to Analyze:
- Are your current channels effective in reaching your target audience?
- Are there additional channels you could utilize (e.g., social media, physical stores)?
- How can you optimize or integrate existing channels for a seamless customer experience?
Example: Amazon uses e-commerce platforms, mobile apps, and physical stores (like Amazon Go) to deliver its services.
4. Customer Relationships
This block focuses on how your business interacts with its customers.
- Questions to Analyze:
- What type of relationship do customers expect (e.g., personal, automated, or self-service)?
- How effectively are you engaging with customers to build loyalty?
- Are there gaps in customer satisfaction or retention?
Example: Netflix uses personalized recommendations and automated interactions to strengthen customer relationships.
5. Revenue Streams
Revenue streams detail how your business generates income from its customer segments.
- Questions to Analyze:
- What are your primary and secondary revenue streams?
- Are there new revenue opportunities, such as subscriptions, partnerships, or upsells?
- Are your pricing models competitive and aligned with customer value?
Example: Spotify combines subscription fees (Premium users) and advertising revenue (Free-tier users) as primary income sources.
6. Key Resources
Key resources are the assets required to deliver your value proposition.
- Questions to Analyze:
- What are the most critical resources for delivering your product or service (e.g., physical, intellectual, or financial)?
- Are your resources sufficient to sustain or scale your business?
- Can you optimize resource usage or invest in additional assets?
Example: Apple’s key resources include its intellectual property, talent pool, and robust supply chain.
7. Key Activities
Key activities are the critical tasks your business performs to create and deliver value.
- Questions to Analyze:
- What are the core activities driving your business model?
- Are there inefficiencies in production, marketing, or service delivery?
- How can you innovate processes to enhance productivity?
Example: Airbnb focuses on platform development, host onboarding, and customer support as its key activities.
8. Key Partnerships
Key partnerships include the suppliers, distributors, or collaborators essential for your business’s success.
- Questions to Analyze:
- Who are your most important partners, and what value do they bring?
- Are there potential partnerships you can form to improve operations or expand your reach?
- Can you reduce dependency on certain partners to minimize risks?
Example: Starbucks partners with coffee bean suppliers and distribution networks to maintain its supply chain.
9. Cost Structure
The cost structure outlines all the expenses involved in running your business.
- Questions to Analyze:
- What are your largest cost drivers, and are they justified?
- Are there areas where you can reduce expenses without compromising quality?
- How does your cost structure compare to competitors?
Example: Uber’s cost structure prioritizes platform maintenance, driver incentives, and marketing expenses.
Steps to Perform a Business Model Canvas Analysis
Step 1: Gather Relevant Data
Collect data from internal teams, customer feedback, market research, and competitor analysis. Ensure you have a clear understanding of your operations and customer needs.
Step 2: Complete Each Section
Using the nine components of the BMC, fill in the current state of your business. Be as specific and data-driven as possible.
Step 3: Identify Gaps and Opportunities
Analyze each component to identify strengths, weaknesses, and growth opportunities. Pay attention to areas where your business could optimize or innovate.
Step 4: Develop an Action Plan
Prioritize the most critical areas for improvement. Create a plan with measurable goals, timelines, and assigned responsibilities.
Step 5: Test and Iterate
Implement changes on a small scale before rolling them out broadly. Continuously refine your business model based on performance and feedback.
Benefits of Business Model Canvas Analysis
- Holistic Understanding: Provides a complete view of your business operations and interdependencies.
- Improved Decision-Making: Helps identify where to focus resources for maximum impact.
- Increased Agility: Enables faster adaptation to market changes and customer demands.
- Enhanced Communication: Acts as a visual tool for aligning teams and stakeholders.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why is business model canvas analysis important?
It helps businesses identify inefficiencies, adapt to market trends, and create strategies for sustainable growth.
2. Can startups use the Business Model Canvas?
Yes, startups benefit greatly from using the BMC as it helps them validate their ideas and focus on scalable components.
3. How often should I conduct a business model canvas analysis?
Ideally, perform an analysis annually or whenever your business undergoes significant changes, such as entering new markets or launching new products.
4. What tools can I use for Business Model Canvas Analysis?
Tools like Miro, Canva, and Strategyzer offer digital templates and collaboration features for conducting BMC analysis.
5. Can I use the BMC for non-profits?
Yes, non-profits can use the BMC to align their mission, value proposition, and operations effectively.
Conclusion
Conducting a thorough business model canvas analysis allows businesses to understand their value, streamline operations, and uncover growth opportunities. By examining each component, from customer segments to cost structures, companies can create a dynamic model that supports innovation and scalability. Regular analysis ensures your business remains competitive, efficient, and aligned with market demands.



![Top 25+ Elder Care Business Opportunities [Updated 2025] Top 10 Elder Care Business Opportunities](https://businessher.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/1b416bb2f666673524a40ab7f587ec5c-150x150.jpg)














Post Comment